Introduction
Digital transformation (DX) has become the go-to strategy for businesses seeking to improve agility, streamline operations, and engage customers in new ways. As we are at the dawn of the fourth industrial revolution i.e. industry 4.0 where businesses are realigning their digital investments and priorities.
One of the most impactful ways to embark on your DX journey is through predictive maintenance. It goes beyond traditional preventive maintenance by leveraging data and advanced technologies to predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach empowers businesses to optimize maintenance schedules, minimize downtime, and ultimately save millions of dollars.
When a manufacturing company plans to implement a strategy to tackle its uptime issues and enhance its external service offerings, starting by upgrading its preventive maintenance processes is an excellent approach.
A report by the
US Department of Energy highlights that implementing a strong predictive maintenance (PdM) program can lead to a tenfold return on investment (ROI), reduce breakdowns by 70%, cut downtime by 35%-45%, and lower maintenance costs by 25%-30%.

Source: US Department of Energy
The High Cost of Downtime
Traditional preventive maintenance relied on scheduled inspections and maintenance at predetermined intervals, regardless of the actual condition of the equipment. While this approach offers some level of control, it can be inefficient and costly. Unexpected equipment failures, on the other hand, can be even more disruptive. Unplanned downtime leads to a domino effect of problems, including:
- Production stoppage: A brief shutdown can significantly impact production output, leading to missed deadlines and lost revenue.
- Increased repair costs: Reactive repairs are often more expensive than proactive maintenance, as they may involve replacing damaged parts or addressing secondary issues caused by the initial failure.
- Inventory disruptions: Downtime can disrupt your ability to fulfill orders, leading to stockouts and customer dissatisfaction.
- Improved Safety and Compliance: A proactive maintenance strategy not only minimizes downtime but also ensures a safer working environment. Regular checks can prevent accidents caused by equipment failure, leading to fewer workplace injuries and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently and consumes less energy. By adopting preventive maintenance, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs, contributing to environmental sustainability and energy savings.
- Enhanced Equipment Lifespan: Regular maintenance extends the service life of machinery, delaying the need for costly replacements. This long-term perspective on equipment management results in substantial cost savings and a better return on investment.
- Predictive Maintenance Insights: Integrating predictive maintenance with traditional approaches leverages data analytics and machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur. This method allows for maintenance to be scheduled at the most opportune times, further reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Improved Customer Trust and Brand Reputation: By ensuring reliable production schedules and order fulfillment, companies can build stronger relationships with their customers. A reputation for reliability and quality can differentiate a brand in competitive markets.
The statistics around unplanned downtime are staggering. A report by the Department of Energy highlights that unplanned downtime can cost businesses hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour. A separate study by GE revealed that manufacturing organizations experience an average of 800-1000 hours of downtime annually, translating to millions of dollars in lost revenue. These figures clearly illustrate the importance of taking a proactive approach to equipment maintenance.
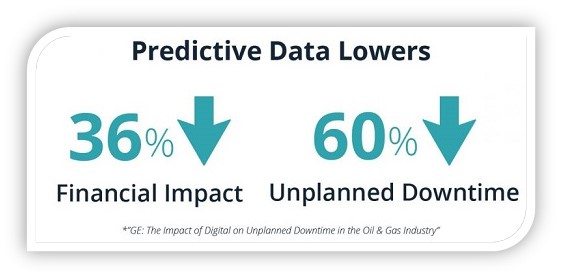
Source: GE
The Power of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a data-driven approach to maintenance that makes use of real-time sensor data and
AI-driven predictive analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail. This allows businesses to schedule maintenance interventions only when necessary, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime. Here's how PdM aka Predictive Maintenance works:
- Data Acquisition: The foundation of PdM lies in data collection. Sensors are installed on critical equipment to monitor various parameters such as vibration, temperature, and energy consumption.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): These sensors are often part of an interconnected IIoT network, facilitating real-time data transmission to a central hub for analysis.
- Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning (ML): Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are applied to the collected data. Historical data is used to establish normal operating patterns for the equipment. Deviations from these baselines can be indicative of potential problems.
- Predictive Insights: By analyzing trends and patterns in the data, ML algorithms can predict equipment failures with a high degree of accuracy. This enables businesses to schedule maintenance interventions before failures occur, preventing costly downtime.
- Customized Maintenance Schedules: PdM allows for the creation of tailored maintenance schedules that match the specific needs of each piece of equipment. This customization goes beyond a one-size-fits-all approach, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
- Asset Performance Management (APM): Incorporating APM tools in conjunction with predictive maintenance enables businesses to optimize the performance of their assets throughout their lifecycle. APM provides deeper insights into asset health, performance, and risk management.
- Reduction in Spare Parts Inventory: By predicting maintenance needs accurately, companies can keep a lean inventory of spare parts. This approach reduces the capital locked up in inventory and minimizes storage costs while ensuring parts are available when needed.
- Enhanced Worker Productivity: Predictive maintenance schedules interventions at optimal times, reducing the burden on maintenance teams. This efficiency allows skilled workers to focus on preventive measures and improvements, rather than emergency fixes.
- Integration with Enterprise Systems: Integrating PdM systems with other enterprise management systems (such as ERP) enhances decision-making. This integration provides a holistic view of maintenance needs in relation to production schedules, supply chain logistics, and financial planning.
- Future-Proofing Through Scalability: PdM technologies are scalable, allowing businesses to start with critical assets and expand as needed. This scalability ensures that companies of all sizes can benefit from predictive maintenance, from small-scale operations to multinational corporations.
- Sustainability Benefits: By optimizing equipment operation and reducing energy consumption, predictive maintenance contributes to a company’s sustainability goals. Efficient operations mean lower carbon emissions and a reduced environmental footprint.
Benefits Beyond Cost Savings
While cost reduction is a significant benefit of PdM, the advantages extend far beyond simply saving money. Here's how a well-implemented PdM program can transform your business:
- Improved Equipment Performance and Lifespan: By proactively addressing potential issues, PdM helps to prevent major breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Predictive Maintenance can identify inefficiencies in equipment operation, allowing you to optimize energy usage and lower your utility bills.
- Optimized Maintenance Practices: PdM empowers you to shift from calendar-based maintenance to a condition-based approach. This reduces unnecessary maintenance activities and frees up resources for other tasks.
- Increased Overall Production Efficiency: By minimizing downtime and optimizing equipment performance, PdM leads to a significant boost in overall production efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety and Compliance: Predictive maintenance not only optimizes operations but also significantly improves workplace safety. By preventing equipment failures, it reduces the risk of accidents, ensuring a safer environment for employees and compliance with health and safety regulations.
- Quality Improvement: By maintaining equipment in optimal condition, PdM contributes to the production of higher quality products. Consistent operation within specified parameters ensures that variations in product quality are minimized, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: PdM generates vast amounts of data on equipment health and performance, providing valuable insights that can inform strategic decisions. This data-centric approach enables businesses to make informed decisions about asset management, investment, and operational strategies.
- Workforce Empowerment: Equipping maintenance teams with predictive insights and actionable data enables them to take a more proactive role in equipment care. This empowerment can lead to higher job satisfaction, improved morale, and a culture of continuous improvement.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: By ensuring that production schedules are met reliably, PdM helps to streamline supply chain operations. Reduced downtime means that delivery schedules are more predictable, which can improve relationships with suppliers and customers alike.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that effectively implement PdM can achieve a significant competitive advantage. The ability to guarantee reliability and high quality can differentiate a business in the marketplace, attracting and retaining customers.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The PdM approach is scalable, allowing businesses to start small and expand as their needs grow. This scalability ensures that PdM can be adapted to the changing needs of the business, providing flexibility in asset management.
The Digital Transformation Journey with PdM
Predictive maintenance isn't just a standalone technology; it's a key component of the broader Industry 4.0 movement. Industry 4.0 refers to the ongoing automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. PdM aligns perfectly with this vision by leveraging data and connected technologies to create a smarter, more efficient production environment.
A prime example of successful PdM implementation comes from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The center utilizes a robust predictive maintenance program for its critical cooling systems. Sensors monitor the performance of equipment like cooling towers and pumps, providing valuable insights into potential maintenance needs. These insights allow for proactive interventions, preventing costly equipment failures and minimizing downtime. The program has demonstrably reduced maintenance costs for NASA, highlighting the tangible benefits of PdM.
Beyond the significant success at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center, another compelling case of PdM application can be observed in the automotive industry. A leading car manufacturer has integrated predictive maintenance into its assembly lines to monitor the condition of robots and other critical machinery. By analyzing data from sensors and applying machine learning algorithms, the system predicts potential breakdowns, allowing for maintenance actions to be scheduled at the most opportune times, thus avoiding unscheduled downtimes, and ensuring continuous production flow.
Furthermore, the integration of PdM with other Industry 4.0 technologies, such as digital twins, allows for the creation of a virtual representation of physical assets. This enables more accurate simulations and analyses, leading to better-informed decisions and strategies. The synergy between PdM and digital twins exemplifies the convergence of physical and digital worlds, a hallmark of Industry 4.0.
PdM is not just a tool for maintaining equipment; it's a strategic asset that drives digital transformation, operational excellence, and sustainable competitive advantage in the era of Industry 4.0. By adopting predictive maintenance, organizations are not only mitigating risks but also embracing a culture of proactive innovation, positioning themselves at the forefront of the fourth industrial revolution.
Getting Started with Predictive Maintenance
Transitioning to a PdM program requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Identify Critical Assets: Begin by prioritizing the equipment that is most critical to your operations. Focus on machinery with a high risk of failure or those responsible for significant production bottlenecks.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Invest in sensor technology to collect real-time data from your chosen equipment. Partner with a data analytics specialist to establish a system for analyzing and interpreting this data.
- Develop a Maintenance Plan: Develop a proactive maintenance plan. This plan should outline specific actions to be taken when certain thresholds are crossed or anomalies are detected.
- Invest in Training: Equip your maintenance personnel with the skills and knowledge necessary to interpret data and implement the PdM program effectively.
- Technology Integration: Ensure seamless integration of PdM technology with existing systems, such as ERP or CMMS, to facilitate data sharing and improve workflow efficiency. This integration enables a more cohesive operation, allowing for automated work orders and maintenance alerts.
- Pilot Testing: Before full-scale implementation, conduct a pilot test on a selected set of assets. This helps in validating the PdM approach, understanding potential challenges, and adjusting strategies based on real-world performance and outcomes.
- Performance Monitoring: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to regularly assess the effectiveness of the PdM program. Metrics might include downtime reduction, maintenance cost savings, and improved asset lifespan.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage all relevant stakeholders, including management, maintenance teams, and IT staff, from the early stages. Clear communication about goals, expectations, and benefits helps in building support and ensuring the successful adoption of PdM practices.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Given the reliance on IoT devices and digital technologies, implementing robust cybersecurity measures is critical to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the PdM system.
- Continuous Improvement: Treat PdM as an evolving program. Regularly review and refine maintenance strategies based on new data insights, technological advancements, and changing operational needs. Encourage feedback from the maintenance team to identify opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion
The digital revolution is upon us, and predictive maintenance (PdM) sits at the forefront. By transitioning from reactive repairs to proactive interventions, businesses can unlock tons of benefits: minimized downtime, extended equipment life, and significant cost savings. PdM isn't just a technology; it's a strategic shift towards a data-driven future.
At
Futurism Technologies, we understand the evolutionary power of predictive maintenance. With nearly two decades of experience in digital transformation, we have a proven track record of helping businesses across various sectors leverage cutting-edge technologies to optimize operations and achieve their DX goals.
We offer a comprehensive suite of Predictive Maintenance solutions, including:
- AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
- IoT solutions
- Data collection
- Data analytics and machine learning expertise
- Development of customized PdM programs
- Training and ongoing support
Ready to take the next step?
Contact us today and discover how PdM can revolutionize your business.

