Agentic AI and Generative AI: What’s Best for Your Business?

Futurism Technologies
July 16, 2025 - 4.2K
5 Min Read
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the way we live and work but not all AI works the same way. Two important types of AI Agentic AI and Generative AI are making big waves but they do very different things. What makes them different and why should you care?
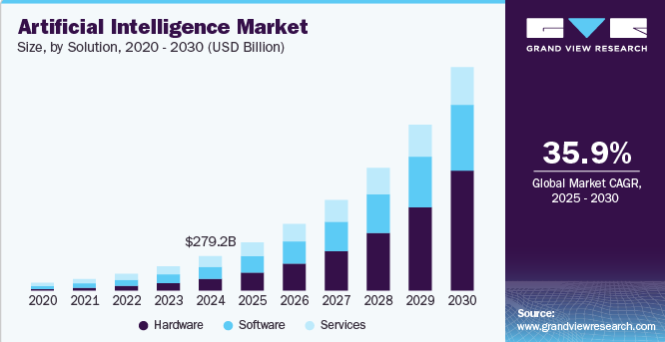
The AI market is booming and is expected to be worth over $1.8 trillion by 2030, growing fast every year. AI isn’t just a thing of the future anymore it’s already changing industries like healthcare, banking and more. As AI keeps improving, people are hearing about Agentic AI and Generative AI more often. Even though they sound similar they have unique strengths and purposes.
Whether you’re someone who loves tech, works in business or just curious about AI, knowing the difference between these two types will help you understand how AI will shape the future.
In this blog, we’ll explain what Agentic AI and Generative AI are, how they work, where they’re used and what they mean for businesses. By the end you’ll have a clear idea of these AI types and how they could impact your world.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI describes AI systems that operate independently, making decisions and taking actions much like a human agent would. Unlike conventional AI, which simply follows instructions, Agentic AI has the ability to set its own objectives, assess changing situations and respond accordingly in real-time environments.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI:
- Autonomy: Works on its own, adapting to changes without needing help.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: Pursues defined objectives potentially adjusting strategies mid-way.
- Environment Interaction: Senses and responds to changes simulating decision making akin to humans or intelligent agents.
- Learning and Adaptation: Employs reinforcement learning and other techniques to improve performance over time.
Examples of Agentic AI include autonomous vehicles navigating traffic, robotic process automation tools optimizing workflows and intelligent assistants managing complex tasks.
Advanced Insights on Agentic AI
Intentionality and Self-Motivation
Unlike traditional AI models that react to inputs, Agentic AI demonstrates a degree of intentionality it can set its own sub-goals to achieve a larger objective. This “self-motivation” is critical in complex environments where pre-programmed responses are insufficient.
Ethical Decision-Making and Governance
Agentic AI’s autonomy necessitates advanced frameworks for ethical reasoning, fairness and accountability. Research in machine ethics and explainable AI (XAI) is crucial to ensure these agents act responsibly in real-world scenarios.
Multi-Agent Systems and Collaboration
Agentic AI can operate as part of multi-agent ecosystems where multiple autonomous agents collaborate, compete or negotiate to solve problems this is particularly relevant in smart cities, supply chains and defense.
Limitations in Generalization
While Agentic AI is autonomous, its decision making is often domain-specific and bounded by the scope of its training and environment understanding. It is not yet capable of the broad general intelligence humans possess.
Did you know? By 2027, 60% of large enterprises are expected to deploy Agentic AI systems in autonomous operations, especially in manufacturing, logistics and smart cities.”
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI on the other hand, focuses on creating new content or data based on patterns learned from existing datasets. These systems create content such as text, images, music and code by imitating human creative processes.
Key Characteristics of Generative AI:
- Content Creation: Generates novel outputs like articles, art or synthetic data.
- Pattern Recognition: Learns complex data distributions to produce realistic, contextually relevant results.
- Data-Driven: Depends on vast amounts of training data for quality output.
- Non-Autonomous: Generally requires prompts or inputs to initiate generation but can be integrated into larger autonomous workflows.
Popular examples include OpenAI’s GPT models that create human-like text, DALL-E for image synthesis and AI-driven music composition tools.
Deep Dive into Generative AI
Latent Space Manipulation
Generative AI models operate in a “latent space” an abstract multi-dimensional representation of learned features allowing nuanced control over outputs. This enables sophisticated editing, style transfer and content customization beyond simple generation.
Fine-Tuning and Transfer Learning
Generative AI models can be fine-tuned on specific datasets to tailor outputs for niche industries (e.g., medical report generation, legal document drafting), making them highly adaptable tools for specialized use cases.
Challenges with Hallucinations
One critical limitation is hallucination where generative models produce plausible but factually incorrect or misleading information. This is a major focus area for research and quality control in deploying generative AI for critical applications.
Integration with Human-in-the-Loop Systems
Generative AI often functions best when combined with human oversight content creators, editors or domain experts validate and refine outputs, ensuring relevance and accuracy.
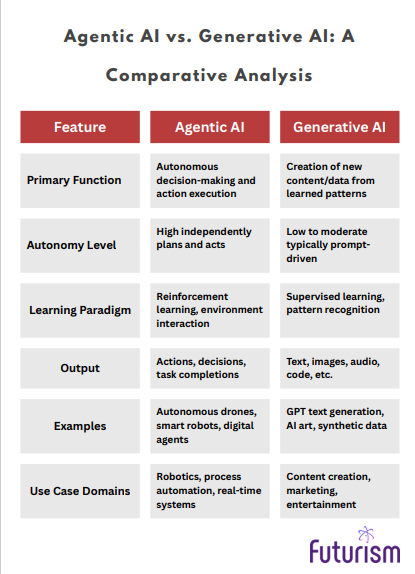
Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: A Comparative Analysis
Though both fall under the AI umbrella, Agentic AI and Generative AI serve different purposes and operate on distinct principles. Below is a systematic comparison to clarify their distinctions:
Real-World Applications: Where Do They Shine?
Agentic AI in Action:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use Agentic AI to see what’s around them, make quick choices and drive safely.
- Industrial Automation: Smart robots adjust their operations in real time to optimize manufacturing processes.
- Personal Assistants: Advanced AI assistants manage schedules, make reservations and learn preferences without constant user input.
- Cybersecurity: Agentic AI detects threats and autonomously responds to mitigate risks.
Generative AI in Action:
- Content Marketing: Creating blog posts, social media content and product descriptions at scale.
- Creative Industries: Designing artwork, composing music or scripting stories.
- Healthcare: Generating synthetic medical data for research without compromising patient privacy.
- Software Development: Assisting developers by generating code snippets and automating documentation.
Strengths and Limitations: A Balanced Perspective
Strengths of Agentic AI
- Proactive and Adaptive: Capable of handling complex, evolving scenarios.
- Efficiency Gains: Automates decision making, reducing human workload.
- Real-Time Responses: Essential for dynamic environments needing quick judgment.
Limitations of Agentic AI
- Complexity: Requires sophisticated programming and massive data.
- Ethical and Safety Concerns: Autonomy raises questions about accountability.
- Resource Intensive: High computational power and sensor integration needed.
Strengths of Generative AI
- Creativity and Scalability: Produces diverse, high-quality content quickly.
- Data Utilization: Uses large amounts of data to discover valuable information.
- User-Friendly: Often simple to prompt and integrate into existing workflows.
Limitations of Generative AI
- Dependence on Data Quality: Poor training data leads to inaccurate outputs.
- Lack of True Understanding: Generates based on patterns without reasoning.
- Potential Bias: Can reflect and repeat the prejudices found in its training data.
Also, explore our detailed guide on AI and Cybersecurity to understand how to address security, ethical, and privacy challenges in AI implementations.
Key Considerations for AI Adoption
Data Privacy and Security
Both Agentic and Generative AI rely extensively on data. Ensuring data privacy and protecting sensitive information is paramount, especially when AI systems operate in regulated industries like healthcare or finance.
Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
Emerging laws (such as the EU’s AI Act) will shape how autonomous and generative AI solutions are developed and deployed, emphasizing transparency, safety and user rights.
Computational Costs and Environmental Impact
Advanced AI models, especially large generative ones, demand significant computational resources, raising sustainability concerns. Efforts toward efficient AI and green AI aim to reduce this footprint.
The Future Outlook: Where is AI Heading?
Agentic AI and Generative AI are not competing but complementary technologies. The future likely holds AI systems that combine both autonomous agents generating creative solutions, reasoning about problems and interacting seamlessly with humans.
Emerging Trends:
- Hybrid Models: AI agents using generative models to brainstorm, simulate scenarios or explain decisions.
- Explainability: Efforts to make AI decisions transparent especially for Agentic AI.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Rules and guidelines that ensure autonomous AI systems are used ethically.
- Human AI Collaboration: Enhancing human creativity and decision making through AI augmentation.
According to market experts by 2026 80% of enterprises plan to integrate AI-driven automation and generative technologies into their digital transformation strategies.
Bonus Tip: Futurism Technologies is at the forefront of harnessing these trends, integrating advanced AI to empower industries with smarter, more adaptive solutions.
Why Understanding These AI Types Matters
For businesses, technologists and policymakers, grasping the distinctions between Agentic and Generative AI is vital:
- Strategic Investment: Selecting the right AI approach based on business needs.
- Risk Management: Addressing ethical, security and operational challenges effectively.
- Innovation Enablement: Leveraging AI’s strengths to unlock new opportunities.
Conclusion
Agentic AI and Generative AI represent two distinct yet powerful frontiers in artificial intelligence. Agentic AI brings autonomy and decision making process, revolutionizing how machines interact with the real world. Generative AI fuels creativity and content generation, expanding AI’s role in communication and entertainment.
Both paradigms have unique strengths and challenges. Together they shape a future where AI is not just reactive but proactive not just imitative but inventive. Staying informed about these developments equips organizations and individuals to navigate the AI revolution with confidence. At Futurism Technologies we are dedicated to guiding enterprises through this evolving landscape delivering AI-powered solutions that are both innovative and responsible.
Make the Most of AI to Grow Your Business. Contact us now and Start Your Digital Transformation Journey Today!
Subscribe Now!
TRENDING POSTS
-
Agentic AI and Generative AI: What’s Best for Your Business?
-
Deepfake Scams: How to Protect Your Business in the Age of AI
-
AI and Cybersecurity: A Strategic Guide for C-Suite Leaders in 2025
-
How Location Intelligence is Revolutionizing BFSI: 6 Must-Know Benefits
-
Cloud and Data Engineering: The Path to Faster Insights and Smarter Decisions
-
From Delays to Innovation: How AI is Optimizing the Construction Industry
-
Data-Driven Future: 6 Trends to Watch Out For
-
The Impact of IoT on Reducing Maritime Carbon Footprints
-
Demystifying SASE: What is Secure Access Service Edge?
-
The Role of AI in Construction Safety
-
What Is Predictive Maintenance and Why Does It Matter?
-
What is Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)? Everything You Need To Know
-
The Role of Smart Maritime IoT Solutions in Enhancing Maritime Safety
-
Revolutionizing Telecom with AI-Driven Network Slicing
-
Data Integration Unlocked: From Silos to Strategy for Competitive Success
-
Navigating the Shadows: Understanding Zero-Click Attacks in the Digital Age
-
AI Reimagined: Crafting Next-Gen AI Apps with Expert Fine-Tuning
-
Futurism AI: Turning Ideas into Apps at Lightning-Fast Speed
-
Accelerate AI Across Your Enterprise With Futurism AI
-
Flying into the Future: How AI is Redefining the Future of Aviation
-
Beyond Intelligence: The Rise of Self-Healing AI
-
The Indispensable Role of a Trusted Offshore AI Company in 2024 & Beyond
-
IoT-Powered Smart Warehouse Management: A Detailed Guide
-
Turning Data into Dollars: The Futurism Path to AI-Driven Success
-
5 Ways to Prepare Your Business for Digital Transformation
-
4 Ways To Win at Digital Transformation on a Shoestring Budget
-
Why AI in Digital Marketing is the Next Big Thing?
-
How AI Will Enable Faster Adaptation of Digital Transformation
-
How Is Digital Modernization Important In Supplier On-Boarding?
-
Top 10 Email Marketing Tips for This Holiday Season
-
Benefits of using ERP Software for Energy and Gas Industries
-
5 Features of Supply Chain Management Software






