Introduction
Introduction
Cloud technology is the backbone of modern business operations. From scalability and flexibility to cost savings, the benefits are undeniable. However, along with these advantages comes the critical challenge of cloud security.
As organizations continue to move their operations to the cloud, cybercriminals are not far behind. Cloud environments have quickly become a prime target for attackers. This guide breaks down the anatomy of a cloud attack, identifies common vulnerabilities, and provides actionable strategies to protect your organization’s cloud infrastructure.
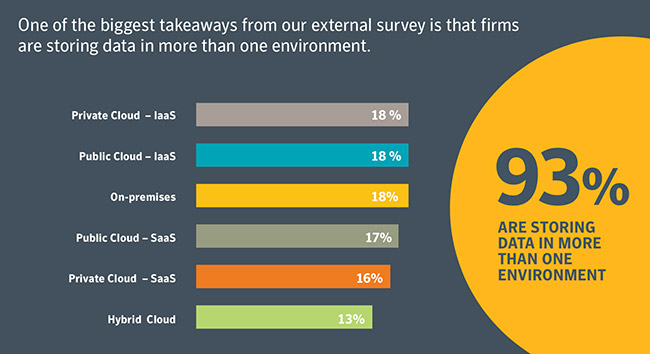
Source: Help Net Security
How a Cloud Security Attack Starts: Recognizing the Signs
How a Cloud Security Attack Starts: Recognizing the Signs
Imagine this: Your organization’s cloud environment is actively monitored, with automated alerts triggered by anomalies like unexpected spikes in data usage or login attempts from unfamiliar locations. One day, your team receives an alert about spikes in outbound data and multiple login attempts from foreign IP addresses.
While this might seem routine, it's a red flag, especially when further investigation reveals that these anomalies were the result of a sophisticated attack.
In this scenario, attackers exploited a series of cloud misconfigurations and human errors to gain unauthorized access. These misconfigurations were not large vulnerabilities on their own, but together they created an opening for cybercriminals.
Fact: 76% of cloud breaches are caused by misconfigurations such as improperly set access permissions or exposed storage buckets. (Source: McAfee)
Breaking Down the Anatomy of a Cloud Attack: Step-by-Step
Breaking Down the Anatomy of a Cloud Attack: Step-by-Step
1. Phishing: The Gateway for Attackers
Phishing remains one of the most common and effective ways for attackers to breach cloud environments. These attacks often come in the form of well-crafted emails disguised as routine communications from trusted sources.
Once an employee clicks on a malicious link and enters their credentials on a fake login page, it’s game over for security.
Statistic: Phishing accounts for 30% of all cloud breaches. (Source: Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report)
2. Escalating Privileges: Gaining Access to Sensitive Resources
Once the attacker has the credentials, they go straight for the Identity and Access Management (IAM) system. Exploiting overly permissive roles, they escalate their privileges to admin level, allowing them to control critical resources. The worst part? They can bypass basic security measures unnoticed.
Fact: 73% of cloud security incidents stem from misconfigured IAM roles. (Source: Gartner)
3. Lateral Movement and Data Exfiltration: Stealth Mode
Armed with administrator-level access, the attacker begins lateral movement, exploring the cloud environment using cloud-native tools like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions. These tools allow them to access sensitive databases, and worst of all, exfiltrate customer data.
Did You Know?
60% of cloud breaches involve data exfiltration, and attackers often use encrypted channels to bypass detection. (Source: Cisco Cloud Security Report)
4. Covering Tracks: The Art of Obfuscation
The final stage is all about covering tracks. The attacker rotates IP addresses, making their movements look like legitimate API calls, and disguising their actions to remain undetected by traditional security systems. This cloud-native stealth makes it difficult for security teams to trace the breach.
Strategic Remediation
Strategic Remediation: How to Stop the Breach and Recover
Once the breach is identified, the priority shifts to stopping the attack and restoring the cloud environment to its secure state. Here’s how to proceed:
1. Containment: Shut Down the Attack
Immediately disable compromised accounts to stop the attacker from moving further within the environment. Isolate affected resources to prevent the breach from spreading.
2. Forensics: Mapping the Breach
A forensic analysis is essential to understand the full scope of the attack. Review logs, audit trails, and API calls to identify where the breach originated and how it evolved. Typically, misconfigured IAM roles will be at the root of the problem.
3. Restoration and Recovery: Rebuilding the Infrastructure
After identifying and isolating the affected systems, restore them from secure backups. Ensure data integrity throughout the recovery process to avoid leaving any remnants of the attacker’s presence.
4. Security Enhancements: Fortify the Cloud
Implement stronger security measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA), revised IAM policies, and real-time monitoring. By improving these areas, you can enhance your defenses and prevent future attacks.
Insights Into the Tactics of Cloud Threat Actors
Insights Into the Tactics of Cloud Threat Actors
Cloud-based attacks are constantly evolving. To defend against them, it’s crucial to understand the tactics employed by modern attackers.
- Leveraging Cloud-Native Services: Attackers are increasingly using serverless computing and cloud-native tools (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) to evade detection and move undetected within the environment.
- Misconfigurations Remain a Major Weakness: A staggering 93% of cloud breaches are attributed to misconfigured cloud services, such as poorly configured IAM roles or unprotected storage buckets. (Source: Accenture).
- Phishing Remains a Powerful Weapon: Attackers are using social engineering tactics to trick administrators into revealing credentials. In fact, 81% of data breaches involve compromised credentials, with phishing being a leading cause. (Source: Verizon)
Cloud Security Best Practices
Cloud Security Best Practices: How to Protect Your Organization
Now that you understand the anatomy of a cloud security attack, it’s time to implement the right safeguards. Follow these best practices to protect your organization from potential breaches:
1. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA should be non-negotiable for all accounts with access to sensitive cloud resources. This single step can reduce the likelihood of a successful attack by 99.9%. (Source: Microsoft)
2. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Audit IAM roles regularly to ensure users only have access to the resources they need. By limiting permissions, you reduce the impact of any breach.
3. Deploy Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Utilize CSPM tools to detect misconfigurations in your cloud environment before attackers can exploit them. These tools automate vulnerability detection and ensure your cloud services remain securely configured.
4. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular
penetration testing helps identify weak spots in your cloud infrastructure. By simulating real-world attacks, you can gain a deeper understanding of potential vulnerabilities and fix them before they become problems.
5. Educate Your Team About Phishing
Since human error is often the biggest risk factor, regularly train employees to recognize phishing attempts. Use email filters to block malicious content and reduce the chances of an employee falling victim to an attack.
6. Back Up Your Data
Always maintain secure backups of critical data. According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach is around $4.24 million. Having a backup plan can drastically reduce both recovery time and costs.
Conclusion
Conclusion: Ready to Secure Your Cloud?
Cloud security is no longer optional. As cybercriminals continue to evolve and develop increasingly sophisticated attack tactics, your organization must stay one step ahead. By implementing the right security practices, you can protect your cloud infrastructure from the next big attack.
At
Futurism Security, we specialize in cloud security solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether it’s tightening your IAM policies, deploying real-time monitoring, or training your team on phishing, we’re here to help.
Ready to secure your cloud? Contact us today for a tailored cloud security audit. Let us help you identify weaknesses, optimize your security controls, and protect your organization from potential breaches.
Contact Futurism Security
Visit www.futurismsecurity.com
