The Ultimate Guide to IoT Security: Keeping IoT Malware at Bay

Futurism Technologies
February 7, 2024 - 4.2K
5 Min Read
The world of cybersecurity is always changing, and now it has got its eye on something new: your smart stuff! From smart devices to connected equipment and smart cities to smart warehouses, ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT) devices are everywhere. Yes! We live in a hyper-connected world where every other device is connected to the Internet.
As we navigate through this hyper-connected world, the stark reality dawns upon us: the very fabric of our digital ecosystem is under constant threat from sophisticated IoT malware attacks, aiming to exploit the inherent weaknesses of these connected and smart devices.
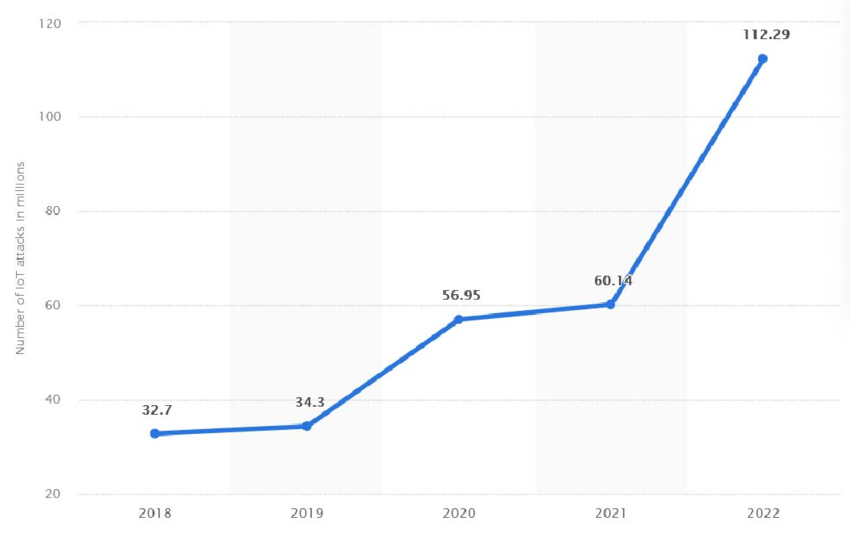
Source: ResearchGate
But there’s need not to worry! This quick handbook will explain everything you need to know about IoT security and IoT malware, why these devices are vulnerable, how hackers exploit them, and most importantly, how to keep your IoT devices safe from these attacks.
Why IoT devices are vulnerable?
IoT devices range from consumer gadgets like smart TVs to industrial control systems and medical devices. Their universal trait is connectivity, allowing remote control and data access. This connectivity, however, becomes a double-edged sword when it comes to IoT security, attracting malicious hackers due to the valuable data these devices handle. The vulnerabilities stem from their limited form factors, lack of built-in security, and the sheer diversity in their hardware, software, and network technologies.
Read also: Industrial IoT under Siege – Navigating Threats and Vulnerabilities
Let’s take a look at some IoT Weaknesses:
Understanding the vulnerabilities is pivotal in crafting robust IoT security measures. Here are the key weaknesses making connected devices vulnerable to IoT malware attacks:
- Device Constraints: Most IoT devices operate with minimal hardware and software capabilities, leaving little room for comprehensive IoT security mechanisms. This limitation makes them easy targets for attacks.
- Hardcoded and Default Passwords: The prevalence of hardcoded and default passwords provides a fertile ground for attackers using brute-force tactics. This vulnerability is exemplified by the HEH botnet, which exploits devices with such credentials.
- Lack of Encryption: IoT devices often transmit or store data in plaintext, exposing them to eavesdropping and manipulation. Lack of encryption jeopardizes the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
- Vulnerable Components: Common hardware components make it easier for attackers to exploit hardware vulnerabilities, posing a significant risk to the device’s security.
- Device Diversity: Diversity in form factors, operating systems, and network technologies among IoT devices demands complex IoT security measures to ensure a standard level of protection.
- Lack of Audit Capabilities: Attackers can compromise IoT devices without leaving traces, as many lack proper audit mechanisms. This covert activity allows them to operate undetected, potentially leading to severe consequences.
- Poor Update Mechanisms: Infrequent vulnerability assessment and penetration testing for secure firmware and software updates expose IoT devices to evolving vulnerabilities. This issue is exacerbated by the extended deployment lifespan of these devices.
- Lack of Security Awareness: Organizations often deploy IoT devices without a comprehensive understanding of their vulnerabilities.
Unmasking IoT Malware and Attacks
The consequences of IoT malware attacks are far-reaching, encompassing botnets, ransomware, destruction ware, and rogue devices.
- IoT Botnets: IoT botnets, exemplified by the infamous Mirai botnet attack in 2016, leverage insecure IoT devices to orchestrate devastating DDoS attacks. The open-source nature of botnet malware makes them a pervasive threat, contributing to over 40% of all DDoS traffic today.
- Ransomware: While some IoT devices may not store valuable data locally, they can still be victims of ransomware attacks. FLocker and El Gato ransomware target mobile phones, tablets, and smart TVs, crippling functionality until a ransom is paid.
- Destructionware: A term coined for IoT malware with the intent to cripple infrastructure, Destructionware aims for political, ideological, or malicious purposes. The 2015 attack on Ukraine’s power grid serves as a stark example of the potential havoc wreaked by such attacks.
- Rogue Devices: Rather than seizing control, cybercriminals may connect rogue devices to unprotected IoT networks, establishing an access point for further infiltration.
Read also: How AI is Transforming Endpoint and IoT Security?
Detection and Prevention of IoT Malware:
The complexity of IoT ecosystem necessitates innovative detection methods. A centralized monitoring system analyzing device activities, coupled with AI-generated behavioral profiles, provides a good foundation. However, in the absence of foolproof detection methods, the focus shifts to preventive strategies. Implementing the following measures significantly enhances IoT device security:
- Enable Strong Authorization: Change default passwords and deploy a strong multifactor authentication system whenever possible to fortify access controls.
- Implement Always-On Encryption: Secure all data and communication channels with constant encryption, reducing the risk of eavesdropping and tampering.
- Disable Unnecessary Features: Minimize the attack surface by disabling unused features, such as Bluetooth when the device communicates via Wi-Fi.
- Apply Patches and Updates: Keep IoT applications and devices up to date, especially firmware. For older devices without update capabilities, isolate them on a separate network to mitigate risks.
- Secure APIs: Stress test and restrict access to APIs, crucial interfaces between devices and back-end systems, ensuring only authorized communication.
- Maintain a Comprehensive Asset Inventory: Recording every IoT device in an inventory tool enhances visibility, aiding in the identification of rogue devices and abnormal traffic patterns.
- Deploy Strong Network Security: Segregate IoT networks and deploy robust network security to thwart unauthorized access.
- Monitor IoT Back-End Apps: Regularly scan for vulnerabilities and set alerts for unusual activity to stay ahead of potential threats.
- Proactive Security Measures: Stay informed about emerging threats and promptly respond to risks with robust EDR/XDR solutions. Establish well-rehearsed plans to detect and respond to ransomware and DDoS attacks.
- Work-from-Home Policies: With the surge in consumer IoT devices connected to home networks, organizations must enforce strict work-from-home policies to mitigate associated risks.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Organize bug bounty programs, rewarding individuals who discover and report vulnerabilities within the IoT ecosystem.
The Future of IoT Attacks
As organizations grapple with the escalating frequency of IoT attacks, a concentrated effort is the need of the hour to establish robust security standards. At Futurism Technologies, we are equipped to help enterprises thwart coming-of-age IoT attacks with market-winning IoT security solutions, be it IoMT security or Endpoint Security, we offer end-to-end IoT security solutions to protect IoT devices from malware attacks.
Navigating the complex realm of IoT security requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding vulnerabilities, implementing preventive measures, and staying abreast of evolving threats, organizations can fortify their defenses against the relentless tide of IoT malware. The future of IoT security hinges on proactive measures, industry collaboration, and adherence to emerging standards.
Get in touch now to secure your IoT devices now!
Subscribe Now!
TRENDING POSTS
-
Futurism Returns to Hannover Messe 2024: Leading the Charge in Industrial and Digital Transformation
-
The Role of Smart Maritime IoT Solutions in Enhancing Maritime Safety
-
Data Integration Unlocked: From Silos to Strategy for Competitive Success
-
Navigating the Shadows: Understanding Zero-Click Attacks in the Digital Age
-
AI Reimagined: Crafting Next-Gen AI Apps with Expert Fine-Tuning
-
Explore Next-Gen Digital Solutions with Futurism at MWC 2024
-
Futurism Unleashes the Technology of Tomorrow at MWC Barcelona 2024
-
Futurism AI: Turning Ideas into Apps at Lightning-Fast Speed
-
Accelerate AI Across Your Enterprise With Futurism AI
-
Futurism to Address the Biggest Security Challenges at RSS 2022
-
Futurism at SelectUSA 2022: Steering the Next Wave of Businesses
-
Futurism to Uplift the MSP Business Community at the MSP Expo 2022
-
Futurism Sets Out to Address the Biggest Security Challenges at the RSA Conference 2022
-
5 Ways to Prepare Your Business for Digital Transformation
-
4 Ways To Win at Digital Transformation on a Shoestring Budget
-
Futurism: Empowering MSPs at the Channel Partners Conference & Expo 2022
-
Why AI in Digital Marketing is the Next Big Thing?
-
Futurism brings ‘Mobile First Digital Transformation’ to the fore at MWC Barcelona 2022
-
Cybersecurity for Rural Hospitals: How can Rural Hospitals become Cyber Smart?
-
Futurism Empowers Rural Health Care Community at the AHA Rural Health Care Leadership Conference
-
The Biggest Problem With Cybersecurity In Healthcare Sector, And How IBM QRadar Can Fix It?
-
How IBM MaaS360 is Revolutionizing Endpoint Security in the Healthcare Industry?
-
Futurism to Present its MSP Partner Program at the Channel Partners Conference & Expo 2021
-
EndPoint Security in Healthcare Matters and IBM MaaS360 Can Help
-
How AI Will Enable Faster Adaptation of Digital Transformation
-
How Is Digital Modernization Important In Supplier On-Boarding?
-
Top 10 Email Marketing Tips for This Holiday Season
-
Benefits of using ERP Software for Energy and Gas Industries